Chatbot Functions
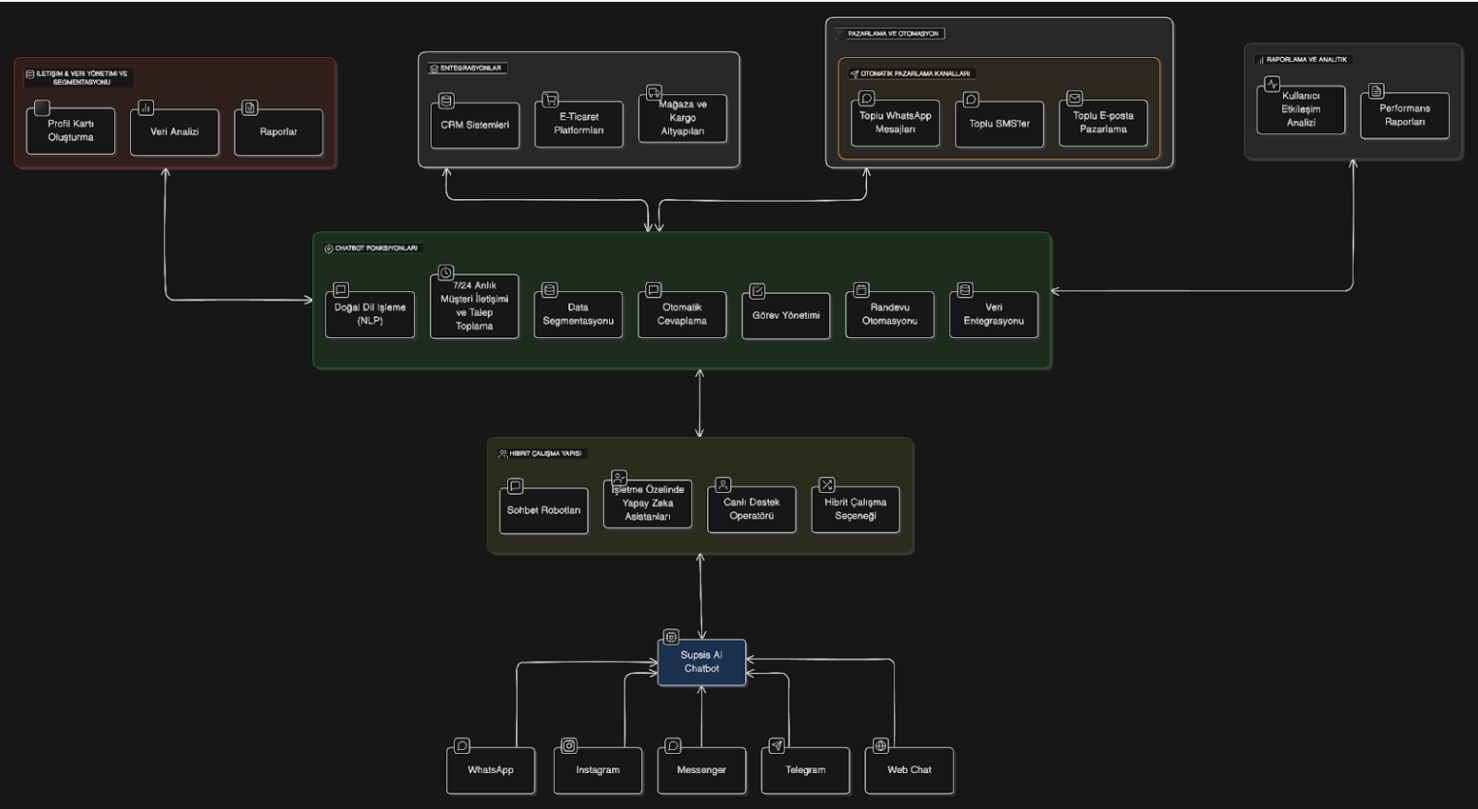
1. Integration Channels
- WhatsApp, Instagram, Messenger, Telegram, Web Chat:
- The chatbot communicates with users through the most popular messaging applications and web chat. This provides access to a wide user base and offers seamless customer service on every platform. A multi-channel strategy is implemented that increases customer satisfaction and strengthens interaction.
- A multi-channel strategy is implemented that increases customer satisfaction and strengthens interaction.
2. Chatbot Functions
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
-
The chatbot uses natural language processing technology to understand users' written expressions. This way, it better analyzes customer requests and provides accurate, personalized responses.
-
24/7 Instant Customer Communication and Request Collection
-
The chatbot provides uninterrupted service, collecting and processing customer requests. This feature increases customer satisfaction while also boosting the business's service speed.
-
Data Segmentation
-
Analyzes user data and divides it into segments. Segmentation is used to offer campaigns and services specific to customers' needs.
-
Automatic Response
-
The chatbot provides automatic responses to frequently asked questions. This lightens the workload of customer support teams and shortens response times.
-
Task Management
-
Converts customer requests into business tasks, tracks them, and directs them to relevant departments.
-
Appointment Automation
-
Provides appointment booking, reminder sending, and calendar management for customers.
-
Data Integration
- The chatbot works integrated with CRM, e-commerce, and other business systems, ensuring data flow and providing dynamic data.
3. Working Structure
-
Chatbots
-
The chatbot answers users' basic questions and offers automatic solutions to solve specific problems.
-
Business-Specific AI Assistants
-
Provides AI solutions optimized for your business content and needs, serving according to industry requirements.
-
Live Support Operator
-
Complex or specific requests are directed to human operators. This way, complex problems are solved more effectively.
-
Hybrid Working Option
- Chatbot and live operators work together. While the chatbot solves basic requests, it transfers complex cases to the operator.
4. Marketing and Automation Channels
- Bulk WhatsApp Messages, Bulk SMS, and Bulk Email Marketing:
- The chatbot communicates directly with users and automatically sends promotional messages, support processes, campaign notifications, and other marketing content based on analysis results. This increases customer interaction and supports marketing strategies.
5. Integrations
- CRM Systems, E-Commerce Platforms, Store and Cargo Infrastructures:
- The chatbot integrates with CRM systems to update customer data, manages order and payment processes through e-commerce platforms. By working integrated with store and cargo infrastructures, it provides tracking of delivery processes.
6. Reporting and Analytics
-
User Interaction Analysis
-
Analyzes customer interactions to measure user behaviors and satisfaction levels. This data is used to improve service quality.
-
Performance Reports
- Analyzes the chatbot's performance and provides detailed reports. These reports guide the improvement of the chatbot and increasing its efficiency.
7. Communication and Data Management & Segmentation
- Profile Card Creation, Data Analysis, Reports:
- Customer profiles are created, analyzed, and reported. This information is used for customer segmentation and providing personalized service. The analyzed data supports marketing strategies and customer satisfaction improvement efforts.
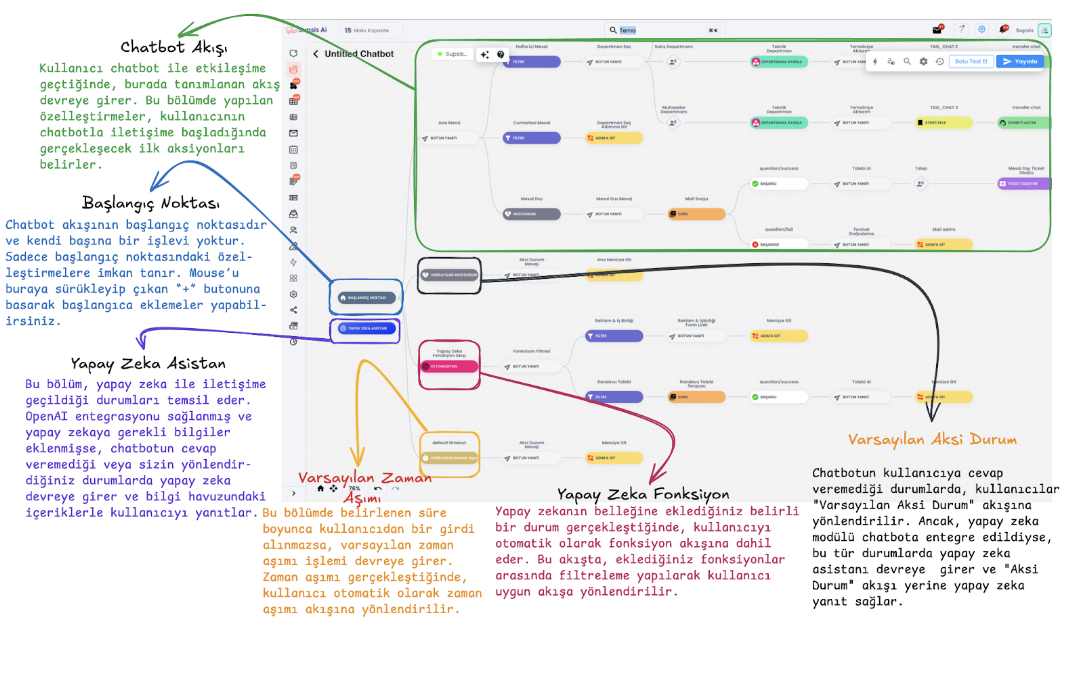
Working Principle and Flow Management of Chatbot Blocks
1. Basic Working Principle of Chatbot Blocks
-
Block Definition
Each block represents an interaction or action. When a user passes through a block, the functions defined in that block are activated.
-
Routing Mechanism
Based on user inputs, response selections, or behaviors, users are directed to appropriate blocks. For example:
When a user clicks a specific button or enters a keyword, the chatbot analyzes this input and provides routing to relevant action blocks.
2. Flow Between Blocks
-
Flow Process
Users' transitions between blocks create a flow. This flow is shaped according to the user's choices and given responses. - Example Flow:
- User responds to a question or clicks a button.
- Chatbot analyzes the response and directs the user input to action blocks.
- After the user responds, they are automatically directed to the block determined as the next step.
3. Creating the Diagram
- Blocks on the diagram are created by dragging and dropping from the right panel. Additionally, appropriate blocks can be selected and added to the diagram using the "+" button on the block.
4. Routing and Interaction Types Between Blocks
Message Sending Blocks
Used to provide responses to users or give information.
-
Routing Blocks
Directs the user to a specific block or URL (e.g., "Go to Block").
-
Filter Blocks
Data is filtered according to user attributes and correct actions are triggered.
-
User Input Definition Blocks
Analyzes user input and provides responses according to specific keywords.
-
Timer Blocks
Controls the speed of responding to user inputs.
5. Diagram Flow Control
-
Correct Routing
Correct routing to blocks should be made to ensure users quickly access the information they need.
-
Interaction Order
Questions and responses presented to the user should be in a logical order.
-
Exit Routes
Alternative routes should be defined so that users don't get stuck in the flow (e.g., "Return to Main Menu").
6. Timeout Management
-
Local Timeout:
If the user doesn't respond within the specified time, the timeout block is activated. -
Default Timeout:
Defined at the beginning of the scenario and triggered in a shorter time than local timeout.
7. Diagram Content Actions
Hover over the button you want to take action on and click the three-dot button in the upper right. Then you can make the appropriate action selection: - ### Collapse Collapses all blocks after the block you're working on. - ### Collapse All Adds collapse feature to all buttons after this block. Click on the relevant block to expand. - ### Edit You can edit content by clicking on the relevant button. - ### Move Moves this block and all the diagram in front of it to another section. - ### Copy Copies the selected block and all the diagram in front of it, you can paste it to another section. - ### Delete/Delete with Internal Branches Delete button only deletes that block, delete with internal branches deletes the entire diagram. - ### Start Test from Here Starts a simulation starting from the block you specified on the bot test screen. - ### Copy Block ID Copies the block's ID. - ### Create Live Link from Here Opens a chatbot simulation screen that will start from this block. Provides webchat experience on the customer test page.
Basic Blocks and Flow
Blocks, which are the basic building blocks of chatbot flow, organize user interactions and manage flow according to different scenarios. These blocks are used to understand user requests, respond, and make correct directions.
Basic Blocks List
1. Chatbot Flow
- Activated when the user interacts with the chatbot and starts the defined flow. The customizations made in this section determine which actions will be activated when the user starts communication.
2. Starting Point
- It is the starting point of the chatbot flow and has no function by itself. Only customizations at the starting point can be made. You can drag the mouse here and press the "+" button to make new additions to the start.
3. AI Assistant
- This block represents situations where communication is established with artificial intelligence. When OpenAI integration is provided, artificial intelligence is activated to answer user questions and integrate into the chatbot flow.
4. Default Timeout
- If no response is received from the user for the duration specified in this section, the default timeout is triggered. The user is automatically directed to the timeout flow.
5. AI Function
- When specific situations you add to the AI's memory occur, it automatically includes the user in the function flow. This flow ensures that the user gets the appropriate response by filtering among the functions you added.
6. Default Otherwise
- When the chatbot cannot respond to the user's question, it automatically directs the user to the "Default Otherwise" flow. If the user gives an input that is not defined to the chatbot and there is a local otherwise in that section, they are directed to the local otherwise flow. However, if local otherwise is not available and AI is integrated into the system, AI provides a response instead of default otherwise.
Interactions
These are blocks that enable the chatbot to interact with users. With these blocks, the chatbot can understand user requests, send messages and files to users, and provide appropriate routing according to user-specific filtering. You can process and classify the received data or the person's data.

Interaction Blocks
Interaction blocks enable the chatbot to communicate with users and respond to user requests. These blocks are used to manage chatbot flow, collect data, and personalize user experience.
Interaction Blocks List
- Bot Response: Sends various responses to the user such as text, image, button, file, or document. This block enables the chatbot to directly respond to user questions and receive requests through buttons.
- AI Response (GPT-4.0): Responds to user questions using the GPT-4.0 model according to the instructions and attributes you provide. This block uses artificial intelligence technology to provide more dynamic and intelligent responses.
- Otherwise: Activated when the user makes an unexpected or undefined input. The Otherwise block directs the user to an alternative flow.
- Timeout: A block triggered after a certain time passes when the user doesn't respond. This block is used to re-engage the user.
- Filter: Filters user data or values like time, providing appropriate routing according to determined criteria.
- Flow: Allows the chatbot to create more complex scenarios. This block makes complex scenarios more organized by putting the determined section of the chatbot into a single flow.
- File Input: Allows the user to upload files. For example, when a user sends a document or image, this file can be stored and processed in the system.